
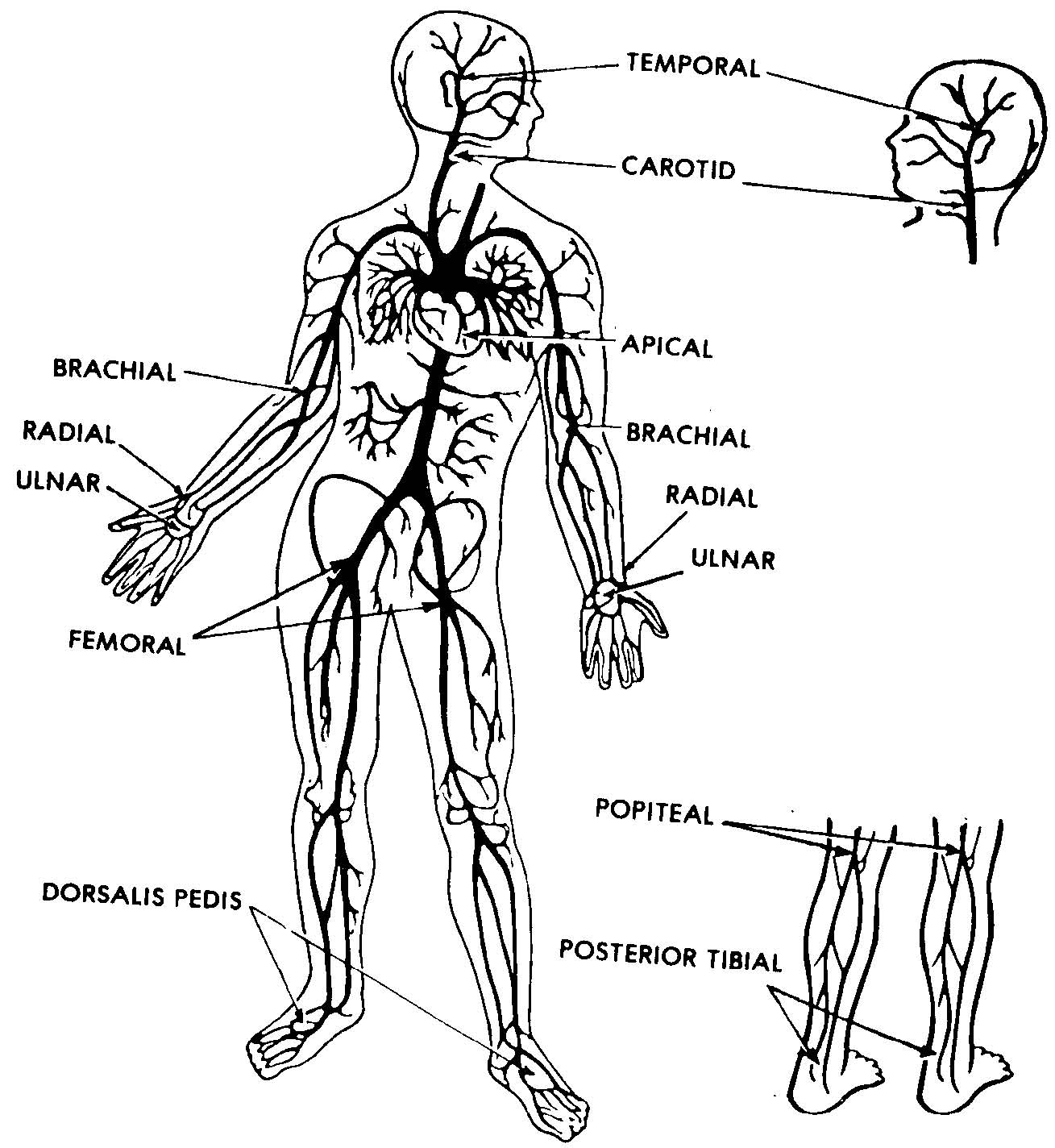
Medications (stimulants increase the pulse rate and depressants decrease the pulse rate)Īrticle about Hemodynamic Monitoring Common pulse pointsĩ most commonly assessed pulse points on the body by nurses are:.
#Radial pulse how to#
Learn how to take pulse rate Factors that affect pulse rate Table 1: How to grade pulse on a scale of 0 – 4+ Slightly more diminished pulse than normal The strength of the pulse also should be graded on a scale of 0 to 4 +.

When you assess the pulse, you are observing for characteristics of the pulse.

The pulse can be defined as a rhythmic wave of pressure formed by the expansion of an artery due to the heart’s contraction of the left ventricle. In this case, a more central site like the carotid artery should be used to check for pulse. The radial pulse you feel from the radial artery is the most common pulse point for taking pulse in adolescents and adults.īut during a cardiovascular collapse, radial pulse usually will not be palpable. The characteristics (eg: abnormally slow, fast, or irregular pulse) of the pulse will give you an indication of the cardiovascular system’s ability to deliver enough blood to the body. Monitoring pulse is a crucial part of physical assessment and observing vital signs. You can feel them by lightly palpating the artery against the underlying bone or muscle. There are 9 common pulse points on the body. It occurs as a result of rapid blood flow within the arteries during the contraction of the heart. The pulse is the palpable throbbing sensation you feel over the peripheral arteries.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
